Biological Therapy in Orthopedics
Overview
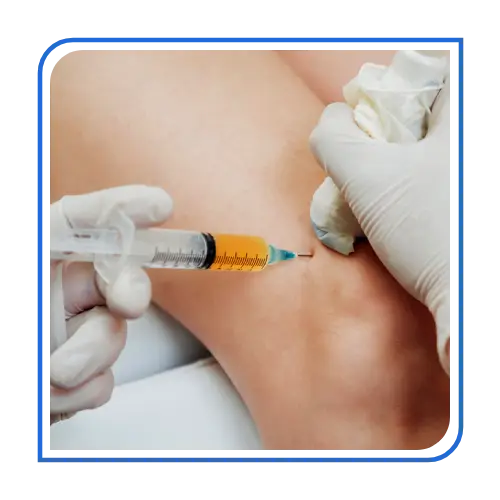
Biological Therapy in Orthopaedics is a cutting-edge treatment approach that utilizes the body’s natural healing mechanisms to repair damaged tissues, reduce inflammation, and improve recovery. It is widely used for conditions such as arthritis, tendon injuries, ligament tears, and cartilage damage. This therapy helps in delaying or even avoiding the need for surgery by promoting natural regeneration.
Key Aspects of Biological Therapy in Orthopaedics:
✅ Growth Factors & Cytokines – Naturally occurring proteins that stimulate tissue repair and reduce inflammation.
✅ Hyaluronic Acid Injections – Improve joint lubrication and reduce pain in osteoarthritis.
✅ Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation (ACI) – Uses a patient’s own cultured cartilage cells to repair cartilage damage.
With Biological Therapy in Orthopaedics, patients can benefit from enhanced healing, reduced pain, improved mobility, and long-term joint preservation—a game-changer in modern orthopaedic care.
Key Aspects of Biological Therapy in Orthopaedics:
✅ Growth Factors & Cytokines – Naturally occurring proteins that stimulate tissue repair and reduce inflammation.
✅ Hyaluronic Acid Injections – Improve joint lubrication and reduce pain in osteoarthritis.
✅ Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation (ACI) – Uses a patient’s own cultured cartilage cells to repair cartilage damage.
With Biological Therapy in Orthopaedics, patients can benefit from enhanced healing, reduced pain, improved mobility, and long-term joint preservation—a game-changer in modern orthopaedic care.
Symptoms Indicating the Need for Biological Therapy
Patients experiencing the following symptoms may benefit from biological therapy
Chronic tendon or ligament injuries
Swelling and inflammation in joints or muscles
Persistent joint pain and stiffness
Difficulty performing daily activities due to pain
Regain mobility and live pain-free! Consult a specialist today.
Conditions Treated with Biological Therapy
Biological therapy is used to manage various orthopedic conditions, including
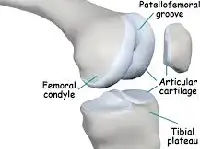
Cartilage Damage
Supports cartilage restoration for improved joint function.
Fractures
Breaks in bones due to high-impact activities.
Sports Injuries
Promotes faster recovery from muscle and ligament injuries.
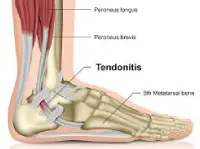
Tendonitis
Accelerates healing of inflamed tendons.
The Process of Biological Therapy in Orthopaedics
Biological therapy follows a structured procedure to ensure optimal results and effective healing.
- Patient Evaluation and Diagnosis – A thorough assessment, including medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests (X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound), is conducted to determine the severity of the orthopedic condition and suitability for biological therapy.
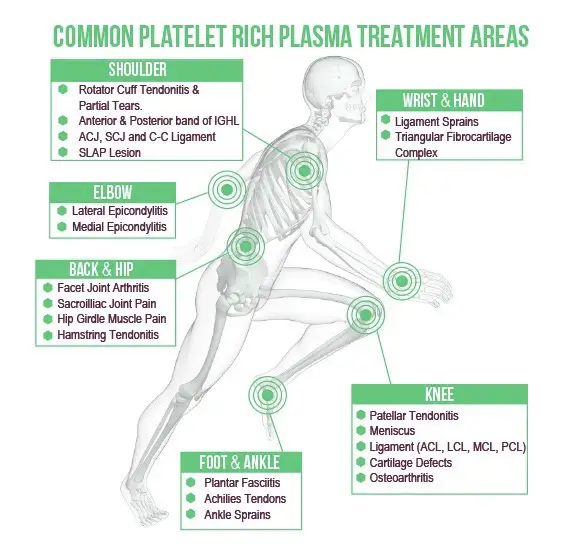
- Selection of Biological Therapy – Depending on the injury, different biological treatments may be used, including Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy, stem cell therapy, bone marrow aspirate concentrate (BMAC), and autologous chondrocyte implantation (ACI).
- Preparation of Biological Agents – If PRP or stem cells are being used, blood or bone marrow is extracted from the patient, processed in a centrifuge to concentrate growth factors or stem cells, and prepared for injection.
- Administration of Treatment – The biological agent is precisely injected into the affected area under ultrasound or fluoroscopic guidance to ensure accurate placement and maximize healing potential.
- Post-Treatment Rehabilitation – Patients follow a customized rehabilitation plan, including physical therapy, activity modification, and nutritional support, to enhance tissue regeneration and recovery.
Advanced in Biological Therapy in Orthopaedics
Biologic-Enhanced Surgeries
Integration of biologic scaffolds enhances ACL and rotator cuff repair outcomes.
Extracellular Vesicles & Exosome Therapy
Exosomes improve cell communication and promote faster recovery.
Tissue Engineering & 3D Bioprinting
Bioprinted cartilage and bone grafts offer patient-specific solutions.
Bone Marrow Aspirate Concentrate (BMAC)
Rich in stem cells and growth factors for osteoarthritis and bone repair.
