Arthoscopy Surgery
Overview
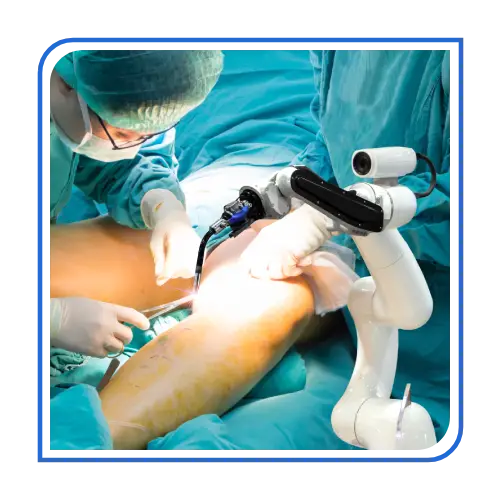
Key Aspects of Arthroscopy Surgery:
✅ Minimally Invasive – Small incisions lead to less pain, faster healing, and minimal scarring.
✅ Faster Recovery – Shorter hospital stays and quicker return to daily activities or sports.
✅ Accurate Diagnosis & Treatment – High-definition visualization helps in precise surgical corrections.
✅ Common Procedures – Includes ligament repairs (ACL, PCL), meniscus surgery, cartilage restoration, and rotator cuff repair.
✅ Lower Risk of Complications – Reduces infection risk compared to open surgery.
With Arthroscopy Surgery, patients experience less pain, quicker mobility restoration, and better long-term joint health—making it a preferred choice for joint treatments.
Symptoms Indicating the Need for Arthroscopy
Patients experiencing the following symptoms may require arthroscopic surgery
Joint instability or weakness
Clicking, locking, or catching sensation in the joint
Swelling and inflammation in the joint
Difficulty performing daily activities due to joint discomfort
Don’t let joint pain limit your life! Consult a specialist today to explore arthroscopy surgery options and restore your movement.
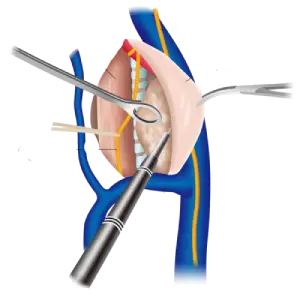
Conditions Treated with Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy is used to diagnose and treat a variety of orthopedic conditions, including
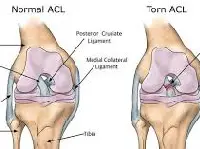
Torn Ligaments (ACL, PCL, Rotator Cuff Tears)
Common in athletes and physically active individuals.
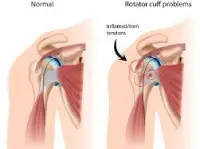
Shoulder Impingement & Rotator Cuff Injuries
Causes pain and limited shoulder movement.
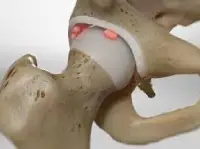
Loose Bone Fragments or Debris
Removal of damaged cartilage or bone pieces from the joint.

Recurrent Dislocations
Repairing unstable joints to prevent future dislocations.
The Arthroscopy Surgery Process
Arthroscopy follows a structured approach to ensure a smooth and effective recovery.
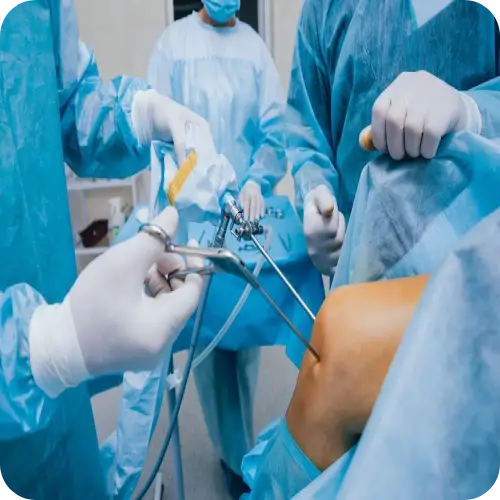
- Patient Evaluation – A thorough assessment, including medical history, physical examination, and imaging (X-ray, MRI, or ultrasound), determines the need for biological therapy.
- Selection of Therapy – Based on the condition, treatments like Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP), Stem Cell Therapy, Bone Marrow Aspirate Concentrate (BMAC), or Tissue Engineering are chosen.
- Preparation of Biological Agents – Blood, bone marrow, or adipose tissue is extracted and processed to concentrate growth factors or stem cells.
- Administration of Treatment – The biological agent is injected into the affected area under ultrasound or fluoroscopic guidance for precise delivery.
- Post-Treatment Rehabilitation – A customized recovery plan, including physiotherapy and activity modification, is followed to enhance healing.
Advanced in Arthroscopy Surgery Process
Biologic Augmentation
Combines arthroscopy with PRP, stem cells, or growth factors to enhance healing.
Robotic-Assisted Arthroscopy
Improves accuracy in ligament reconstruction and joint repair.
Nano-Arthroscopy
Uses ultra-small cameras and instruments for minimally invasive procedures with faster recovery.
High-Definition 4K and 3D Arthroscopy
Provides enhanced visualization for precise surgical intervention.
